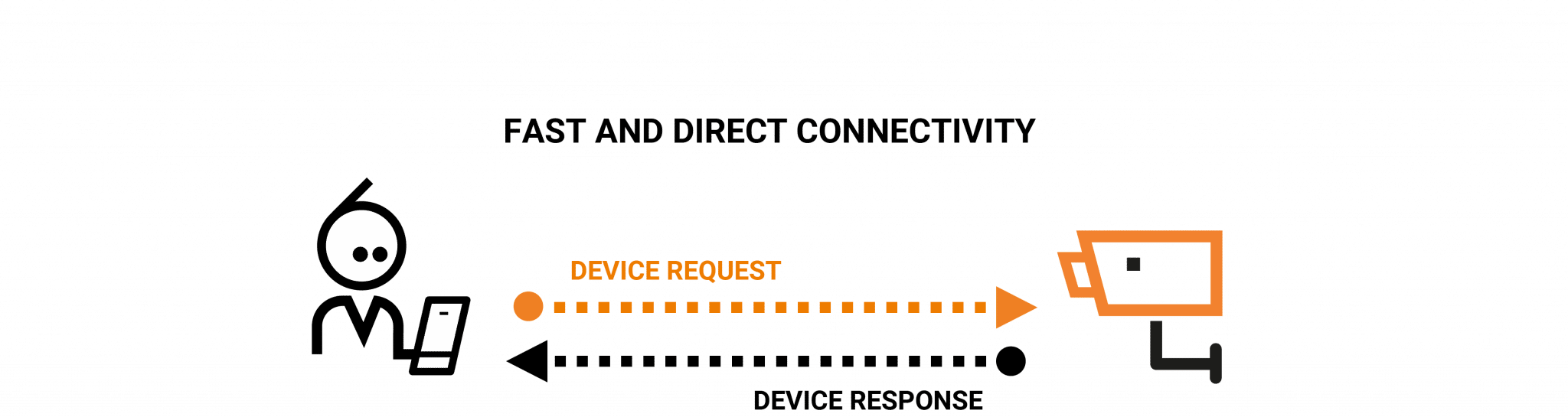
Peer-to-peer (P2P) technology combined with the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way devices interact and share data. This groundbreaking combination is creating a new paradigm in connectivity, enabling seamless communication between devices without centralized control. As IoT continues to expand, P2P technology is playing an increasingly vital role in enhancing efficiency, security, and scalability in smart ecosystems.
IoT P2P is not just a buzzword but a fundamental shift in how devices are interconnected. By leveraging decentralized networks, IoT devices can communicate directly with each other, reducing reliance on traditional server-based architectures. This approach offers significant advantages, including reduced latency, improved data privacy, and enhanced resilience against network failures.
As industries adopt IoT P2P solutions, businesses and consumers alike are benefiting from smarter, more autonomous systems. From smart homes to industrial automation, the potential applications of IoT P2p are vast and continue to evolve. This article explores the concept, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of IoT P2P technology in detail.
Read also:Exploring The Uk Amateur Facials Scene A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT P2P
- What is IoT P2P?
- Benefits of IoT P2P
- Challenges in IoT P2P Implementation
- IoT P2P Use Cases
- Security Considerations in IoT P2P
- Scalability of IoT P2P Networks
- IoT P2P vs Traditional IoT
- The Future of IoT P2P
- Conclusion
Introduction to IoT P2P
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become a cornerstone of modern technology, enabling billions of devices worldwide to connect and exchange data. However, as the number of connected devices continues to grow, traditional centralized architectures face challenges such as increased latency, scalability limitations, and security vulnerabilities. This is where IoT P2P comes into play, offering a decentralized alternative that addresses these issues effectively.
IoT P2P leverages peer-to-peer networking principles to create a distributed system where devices communicate directly with one another without relying on a central server. This approach not only enhances performance but also improves reliability and security. By decentralizing data exchange, IoT P2P networks reduce the risk of single points of failure and enable more efficient resource utilization.
What is IoT P2P?
IoT P2P refers to the integration of peer-to-peer networking protocols with IoT devices. In a P2P network, each device acts as both a client and a server, allowing it to send and receive data directly from other devices. This eliminates the need for intermediaries such as cloud servers or gateways, which are typically required in traditional IoT setups.
Key Characteristics of IoT P2P:
- Decentralization: Devices operate independently, reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure.
- Autonomy: Devices can make decisions locally, improving responsiveness and efficiency.
- Resilience: The absence of a single point of failure makes P2P networks more robust.
- Scalability: P2P architectures can handle large numbers of devices without performance degradation.
Benefits of IoT P2P
IoT P2P technology offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive solution for modern connectivity needs. Below are some of the key benefits:
Read also:Running Man 2025 Cast Korea The Ultimate Guide To The Beloved Reality Show
Improved Performance
By eliminating the need for centralized servers, IoT P2P networks reduce latency and improve overall performance. Devices can communicate directly with each other, ensuring faster data exchange and real-time interactions.
Enhanced Security
P2P networks are inherently more secure than traditional architectures because they do not rely on a central point of control. This reduces the risk of cyberattacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and unauthorized access.
Cost Efficiency
IoT P2P eliminates the costs associated with maintaining centralized servers and infrastructure. This makes it a cost-effective solution for large-scale deployments, especially in industries such as manufacturing and logistics.
Challenges in IoT P2P Implementation
While IoT P2P offers many advantages, there are also challenges that must be addressed to ensure successful implementation. These include:
Complexity in Deployment
Setting up a P2P network requires advanced technical expertise, which can be a barrier for some organizations. Ensuring compatibility between different devices and protocols adds another layer of complexity.
Data Management
In a decentralized network, managing and storing data can be challenging. Developers must design systems that ensure data consistency and availability across all nodes in the network.
Interoperability
IoT devices from different manufacturers often use proprietary protocols, making it difficult to achieve seamless interoperability in a P2P environment. Standardization efforts are underway to address this issue, but progress remains slow.
IoT P2P Use Cases
IoT P2P technology has a wide range of applications across various industries. Below are some of the most promising use cases:
Smart Homes
In smart home environments, IoT P2P enables devices such as thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras to communicate directly with each other. This enhances energy efficiency and improves user experience by allowing devices to respond quickly to changes in the environment.
Industrial Automation
P2P networks are ideal for industrial settings where real-time data exchange is critical. Machines can share status updates and performance metrics directly, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing production processes.
Healthcare
In healthcare, IoT P2P can improve patient monitoring by allowing wearable devices to communicate directly with medical equipment. This ensures timely alerts and interventions, improving patient outcomes.
Security Considerations in IoT P2P
Security is a critical concern in IoT P2P networks due to the decentralized nature of the architecture. While P2P systems are inherently more secure than centralized ones, they are not immune to threats. Below are some security considerations:
Data Encryption
All data exchanged between devices in a P2P network should be encrypted to protect against unauthorized access. Advanced encryption protocols such as AES and RSA are commonly used for this purpose.
Device Authentication
To prevent unauthorized devices from joining the network, robust authentication mechanisms must be implemented. This can include digital certificates, biometric verification, or other secure methods.
Intrusion Detection
Deploying intrusion detection systems (IDS) can help identify and mitigate potential threats in real time. These systems monitor network activity and alert administrators to suspicious behavior.
Scalability of IoT P2P Networks
One of the primary advantages of IoT P2P is its scalability. Unlike traditional architectures, P2P networks can handle large numbers of devices without significant performance degradation. This is achieved through:
Distributed Resource Allocation
Resources such as bandwidth and storage are distributed across all nodes in the network, ensuring efficient utilization and preventing bottlenecks.
Dynamic Node Management
P2P networks can dynamically adjust to changes in the number of connected devices, adding or removing nodes as needed without affecting overall performance.
Load Balancing
By distributing workloads evenly across all devices, P2P networks ensure optimal performance even under heavy loads. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high availability and reliability.
IoT P2P vs Traditional IoT
While both IoT P2P and traditional IoT architectures have their strengths and weaknesses, the choice between them depends on the specific use case. Below is a comparison of the two approaches:
Centralized vs Decentralized
Traditional IoT relies on centralized servers to manage and process data, while IoT P2P uses a decentralized approach where devices communicate directly with each other.
Latency
P2P networks typically offer lower latency than traditional architectures due to the absence of intermediaries. This makes them better suited for real-time applications.
Cost
IoT P2P can be more cost-effective in the long run, as it eliminates the need for expensive server infrastructure. However, the initial setup costs may be higher due to the complexity of P2P systems.
The Future of IoT P2P
As technology continues to evolve, IoT P2P is poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of connectivity. Advances in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and edge computing are expected to further enhance the capabilities of P2P networks, enabling even more innovative applications.
Research is ongoing to address the challenges associated with IoT P2P, such as interoperability and security. Industry collaborations and standardization efforts are crucial to ensuring widespread adoption of this transformative technology.
Conclusion
IoT P2P represents a significant advancement in the field of connectivity, offering numerous benefits over traditional architectures. By enabling direct communication between devices, P2P networks enhance performance, security, and scalability while reducing costs. Despite the challenges associated with implementation, the potential applications of IoT P2P are vast and continue to grow.
We encourage readers to explore the possibilities of IoT P2P further and consider how it can be applied in their respective fields. To stay updated on the latest developments, we invite you to share this article, leave a comment, or explore other resources on our website.