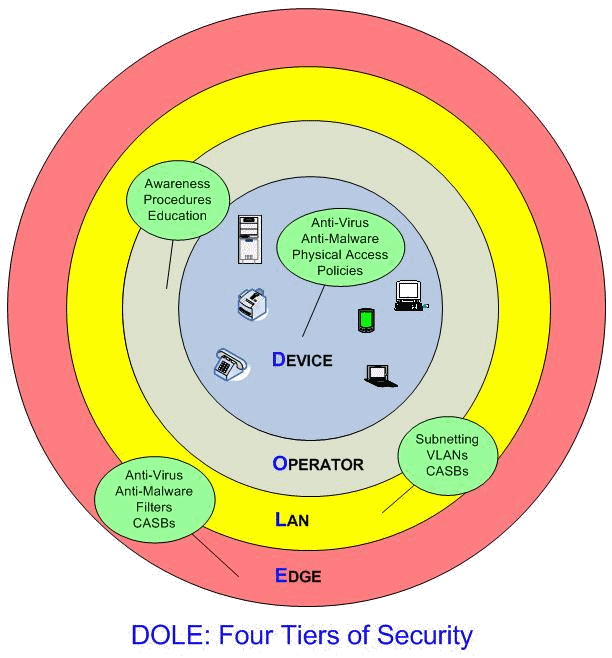
In today's digital landscape, the phrase "from outside the firewall" has become increasingly relevant as more individuals and organizations operate beyond traditional network boundaries. Whether you're accessing work resources remotely, using cloud-based services, or simply navigating the internet, understanding what it means to operate from outside the firewall is crucial. This guide aims to provide you with an in-depth understanding of firewalls, their importance, and how to securely interact with networks from an external perspective.
Operating from outside the firewall can pose significant challenges and risks. However, with the right knowledge and tools, you can ensure that your data remains secure and your activities remain compliant with best practices. This article will cover everything you need to know, from the basics of firewalls to advanced techniques for secure remote access.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the concept, its implications, and actionable steps to protect yourself and your organization when accessing resources from outside the firewall. Let's dive in!
Read also:Nate Robinsons Sports Career A Journey Of Perseverance And Passion
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Firewalls
- Understanding the Concept of Operating From Outside the Firewall
- Common Security Risks When Accessing Data From Outside the Firewall
- Secure Remote Access Methods
- Using VPN Solutions to Safeguard Data
- Cloud Security Considerations
- Best Practices for Safe Remote Operations
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Tools and Technologies for Enhanced Security
- Conclusion
Introduction to Firewalls
A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. Firewalls are essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access.
Types of Firewalls
There are several types of firewalls, each designed to address specific security needs:
- Packet Filtering Firewalls: These firewalls inspect individual packets of data and allow or block them based on specific rules.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: These firewalls track active connections and use this information to make more informed decisions about allowing or blocking traffic.
- Application-Level Firewalls: These firewalls examine data at the application layer, providing deeper inspection capabilities.
Understanding the Concept of Operating From Outside the Firewall
Operating from outside the firewall refers to accessing network resources or data from a location that is not protected by an organization's internal firewall. This could include remote work, mobile devices, or public Wi-Fi networks. Understanding this concept is crucial for ensuring data security and maintaining operational efficiency.
Why Is It Important?
With the rise of remote work and cloud computing, more users are accessing resources from outside traditional network boundaries. This shift increases the potential for security breaches and data leaks, making it vital to implement robust security measures.
Common Security Risks When Accessing Data From Outside the Firewall
Accessing data from outside the firewall comes with inherent risks. Some of the most common security threats include:
- Unsecured Networks: Public Wi-Fi networks often lack proper encryption, making them vulnerable to eavesdropping and data interception.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals frequently use phishing tactics to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software can compromise devices and steal data when connected to unsecured networks.
Secure Remote Access Methods
To mitigate these risks, organizations and individuals can adopt several secure remote access methods:
Read also:Kill Bill Characters A Comprehensive Guide To Tarantinos Iconic Cast
SSH (Secure Shell)
SSH provides a secure channel over an unsecured network by encrypting all data transmitted between devices. It is widely used for remote command-line access and secure file transfers.
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
RDP allows users to remotely connect to another computer over a network connection. While convenient, it is essential to configure RDP securely to prevent unauthorized access.
Using VPN Solutions to Safeguard Data
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure tunnel between a user's device and the network they are accessing. By encrypting all data transmitted through the tunnel, VPNs significantly reduce the risk of data interception.
Choosing the Right VPN
When selecting a VPN, consider factors such as encryption strength, server locations, and user privacy policies. Popular VPN providers include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, and CyberGhost.
Cloud Security Considerations
As more organizations move their operations to the cloud, ensuring cloud security becomes paramount. Key considerations include:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest helps protect sensitive information.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implementing strong IAM policies ensures that only authorized users can access cloud resources.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Best Practices for Safe Remote Operations
Adopting best practices is essential for maintaining security when operating from outside the firewall. Some recommendations include:
- Using strong, unique passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Regularly updating software and firmware to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Avoiding the use of public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive activities.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Organizations must adhere to various legal and regulatory requirements when handling data from outside the firewall. Examples include:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Governs the protection of personal data within the European Union.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): Provides California residents with control over their personal information.
Tools and Technologies for Enhanced Security
Several tools and technologies can enhance security when accessing data from outside the firewall:
Endpoint Protection Platforms
These platforms provide comprehensive protection for endpoints, including antivirus, anti-malware, and firewalls. Examples include Symantec Endpoint Protection and McAfee Total Protection.
Network Security Solutions
Implementing advanced network security solutions, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS), can help identify and block potential threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, operating from outside the firewall requires a thorough understanding of security risks and best practices. By implementing secure remote access methods, using VPN solutions, and adhering to legal and regulatory requirements, you can protect your data and ensure safe operations.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from it and explore additional resources on our website. Together, we can create a safer digital environment for everyone.
Sources: