Welding is a critical skill in modern manufacturing and construction, and having the right Miller welding settings can make all the difference in achieving professional-quality results. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced welder, understanding how to configure your Miller welder for optimal performance is essential. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about Miller welding settings, ensuring you get the best possible outcomes every time.
Welding has been an indispensable process across various industries, from automotive to aerospace. However, achieving high-quality welds requires not only skill but also the proper equipment configuration. Miller welding machines are renowned for their reliability and versatility, but their settings must be adjusted according to the material, thickness, and type of welding you're performing.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of Miller welding settings, covering everything from basic principles to advanced configurations. Whether you're working with mild steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, this guide will help you fine-tune your welder to achieve superior results.
Read also:Unveiling The Cast Of Jeepers Creepers A Deep Dive Into Horror Cinema
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Miller Welding
- Key Components of Miller Welding Settings
- Understanding Welding Materials
- Basic Miller Welding Settings
- Advanced Settings for Professional Results
- Troubleshooting Common Welding Issues
- Miller Welding Settings for Specific Materials
- Tips for Optimizing Miller Welding Settings
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Miller Welding
Miller Electric Manufacturing Company, commonly known as Miller, is one of the most trusted names in the welding industry. Established in 1929, Miller has been at the forefront of welding technology, producing high-quality equipment that caters to both hobbyists and professionals.
Miller welding machines are renowned for their durability, ease of use, and adaptability to various welding techniques. Whether you're using MIG, TIG, or stick welding, Miller offers a wide range of models designed to meet different needs. However, to fully harness the potential of these machines, it's crucial to understand and adjust the settings correctly.
This section will provide an overview of Miller welding equipment and its significance in the welding world, setting the stage for a deeper dive into the settings that make these machines so effective.
Key Components of Miller Welding Settings
Miller welding settings involve several critical components that must be configured correctly to achieve the desired results. These components include voltage, amperage, wire feed speed, shielding gas, and more. Each component plays a specific role in the welding process, and understanding their functions is key to optimizing your welds.
Voltage: Voltage controls the arc length and determines how deep the weld penetrates the base material. Higher voltage results in a longer arc and deeper penetration, while lower voltage creates a shorter arc and shallower penetration.
Amperage: Amperage, or current, affects the heat input during welding. Higher amperage increases the heat, which is ideal for thicker materials, while lower amperage is suitable for thinner materials.
Read also:Real Housewives Of Beverly Hills Ages 2024 The Ultimate Guide To The Stars
Other components such as wire feed speed and shielding gas selection also play crucial roles in the welding process. By carefully adjusting these settings, you can achieve clean, strong welds that meet industry standards.
Understanding Welding Materials
One of the most important factors in determining Miller welding settings is the type of material you're working with. Different materials require different settings to ensure proper fusion and avoid defects such as cracking or porosity.
Mild Steel: Mild steel is one of the most commonly welded materials due to its affordability and versatility. It requires lower voltage and amperage settings compared to harder materials.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel welding demands specific settings to maintain its corrosion-resistant properties. Higher amperage and proper shielding gas are essential for stainless steel welding.
Aluminum: Aluminum welding presents unique challenges due to its high thermal conductivity and tendency to oxidize. Specialized settings, including higher voltage and specific shielding gases, are necessary for successful aluminum welds.
Basic Miller Welding Settings
For beginners, mastering basic Miller welding settings is the first step toward achieving professional-quality welds. Here are some fundamental settings to consider:
- Voltage: Start with a moderate voltage setting and adjust based on material thickness.
- Amperage: Begin with a low amperage and gradually increase as needed for thicker materials.
- Wire Feed Speed: Adjust the wire feed speed to match the amperage and material being welded.
- Shielding Gas: Choose the appropriate shielding gas for the material (e.g., 75% argon/25% CO2 for mild steel).
These basic settings serve as a foundation, but remember that adjustments may be necessary depending on the specific application and material.
Advanced Settings for Professional Results
For experienced welders, fine-tuning advanced Miller welding settings can elevate weld quality to new heights. Advanced settings often involve more precise control over parameters such as pulse welding, inductance, and contact tip-to-work distance.
Pulse Welding: Pulse welding involves alternating between high and low currents, which helps control heat input and reduce distortion. This technique is particularly useful for thin materials and intricate welds.
Inductance: Inductance affects the arc force and can be adjusted to achieve better control over the weld pool. Higher inductance results in a softer arc, while lower inductance creates a stiffer arc.
By experimenting with these advanced settings, professional welders can achieve exceptional results that meet the highest industry standards.
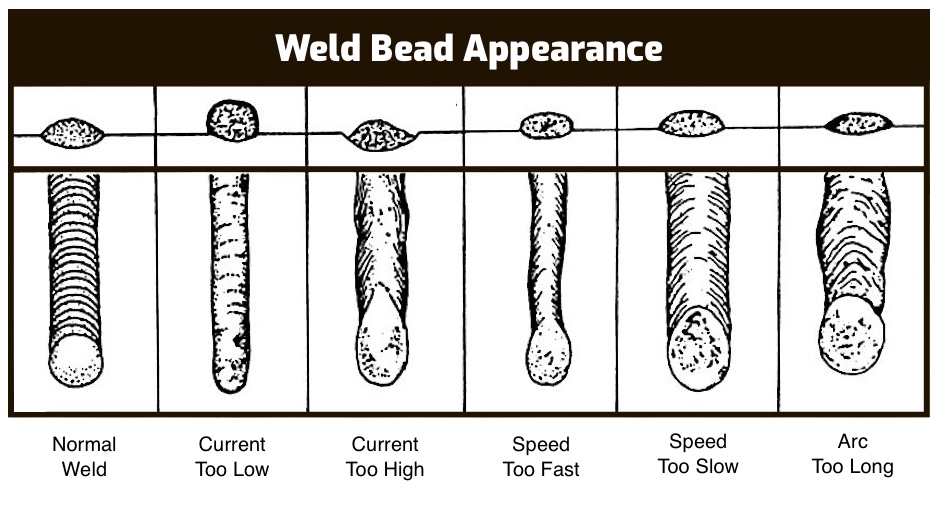
Troubleshooting Common Welding Issues
Even with the correct Miller welding settings, issues can arise during the welding process. Common problems include poor penetration, excessive spatter, and porosity. Here are some troubleshooting tips to address these issues:
- Poor Penetration: Increase voltage or amperage to improve penetration.
- Excessive Spatter: Check wire feed speed and shielding gas settings to reduce spatter.
- Porosity: Ensure proper shielding gas flow and clean the base material to prevent porosity.
By identifying and addressing these issues promptly, you can maintain consistent weld quality and avoid costly rework.
Miller Welding Settings for Specific Materials
Miller Settings for Mild Steel
Mild steel is a popular choice for many welding applications due to its ease of use and affordability. For optimal results, use the following settings:
- Voltage: 18-22 volts
- Amperage: 100-150 amps
- Wire Feed Speed: 150-250 inches per minute
- Shielding Gas: 75% argon/25% CO2
These settings provide a balance between penetration and heat input, ensuring clean and strong welds on mild steel.
Miller Settings for Stainless Steel
Welding stainless steel requires specific settings to preserve its corrosion-resistant properties. Consider the following:
- Voltage: 20-24 volts
- Amperage: 120-180 amps
- Wire Feed Speed: 200-300 inches per minute
- Shielding Gas: 90% argon/10% CO2
These settings help maintain the integrity of the stainless steel while achieving strong welds.
Miller Settings for Aluminum
Aluminum welding presents unique challenges, but with the right settings, you can achieve excellent results. Use the following guidelines:
- Voltage: 22-26 volts
- Amperage: 150-250 amps
- Wire Feed Speed: 300-400 inches per minute
- Shielding Gas: 100% argon
These settings account for aluminum's high thermal conductivity and susceptibility to oxidation, ensuring successful welds.
Tips for Optimizing Miller Welding Settings
Optimizing Miller welding settings involves more than just adjusting voltage and amperage. Here are some additional tips to enhance your welding experience:
- Regularly clean the base material to remove contaminants that can affect weld quality.
- Use high-quality welding consumables to ensure consistent performance.
- Practice proper welding techniques, such as maintaining the correct travel speed and angle.
By following these tips, you can maximize the potential of your Miller welder and achieve professional-grade results.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced welders can fall prey to common mistakes that affect weld quality. Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
- Using incorrect shielding gas, which can lead to porosity and weak welds.
- Setting amperage too high, resulting in burn-through or excessive heat distortion.
- Ignoring proper safety protocols, which can lead to accidents or health hazards.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures safer and more effective welding operations.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Mastery of Miller welding settings is essential for achieving high-quality welds across various materials and applications. By understanding the key components, adjusting settings according to material type, and following best practices, you can elevate your welding skills to professional levels.
We encourage you to experiment with different settings and techniques to find what works best for your specific projects. Don't hesitate to share your experiences and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more in-depth information on welding techniques and equipment.
Remember, practice makes perfect. Keep honing your skills, and with the right Miller welding settings, you'll be welding like a pro in no time!